Everything You Need to Know About the Boiler Installation Part 2 Types of Boilers for Installation
Introduction:
Boilers are an essential component of any home’s heating system. They provide warmth and comfort during the cold winter months. However, with the wide variety of boilers available in the market, it can be overwhelming to choose the right one for your home.
Whether you’re a homeowner looking to replace an old boiler or a new homeowner considering a boiler installation, this comprehensive guide will provide you with all the information you need to make an informed decision. From understanding the importance of professional boiler installation (see here) to exploring different types of boilers and their installation processes, we’ve got you covered.
In this, second part , we will explore the different types of boilers for installation – combi, system, and regular boilers – and discuss their pros and cons. By understanding the characteristics of each type, you will be able to determine the most suitable boiler for your home’s heating needs.
Types of Boilers for Installation:
Boilers are categorized into three main types: combi, system, and regular boilers. Combi boilers are compact and provide both heating and hot water on demand. System boilers are suitable for larger homes and have a separate hot water storage cylinder. Regular boilers, also known as conventional or traditional boilers, require a separate hot water cylinder and cold water storage tank. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the right one depends on factors such as the size of your home, hot water demand, and available space.
1. Combi Boilers
Combi boilers, short for combination boilers, are the most popular choice for smaller homes or apartments. They are compact and do not require additional storage tanks, making them space-efficient. Combi boilers heat water directly from the mains, eliminating the need for a separate hot water cylinder. This feature ensures hot water on demand, making them ideal for households with limited hot water requirements. Additionally, combi boilers are energy-efficient as they only heat the water needed, reducing energy wastage.
For example, a small apartment with limited space and a low hot water demand would benefit from a combi boiler. The compact size and on-demand hot water feature make it a practical choice.
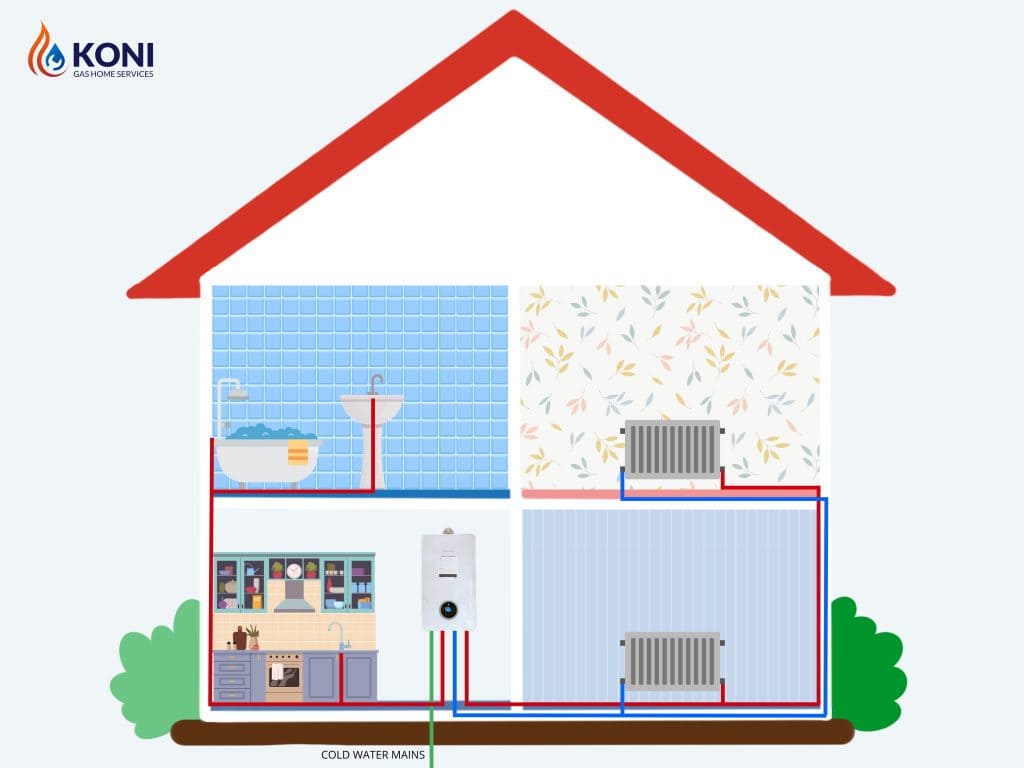
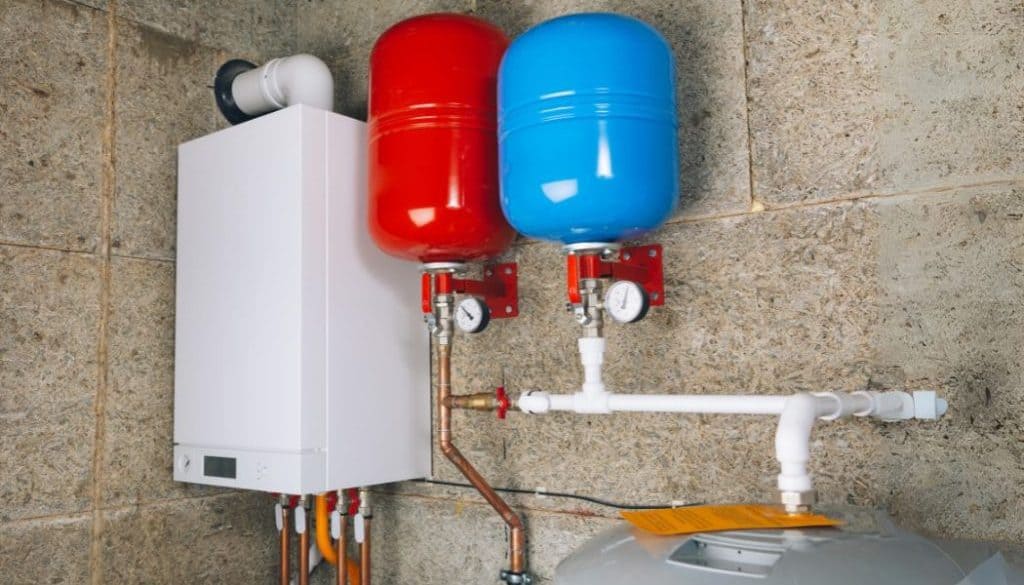
2. System Boilers (Unvented)
System boilers are suitable for larger homes with multiple bathrooms and higher hot water demand. They work by heating water and storing it in a separate hot water cylinder, ensuring a constant supply of hot water. System boilers are compatible with solar water heating systems, making them an eco-friendly option. They also provide better water pressure compared to combi boilers, making them suitable for homes with multiple showers or baths.
For instance, a family home with three bathrooms and a high hot water demand would benefit from a system boiler. The separate hot water cylinder ensures a constant supply of hot water, even with multiple showers running simultaneously.

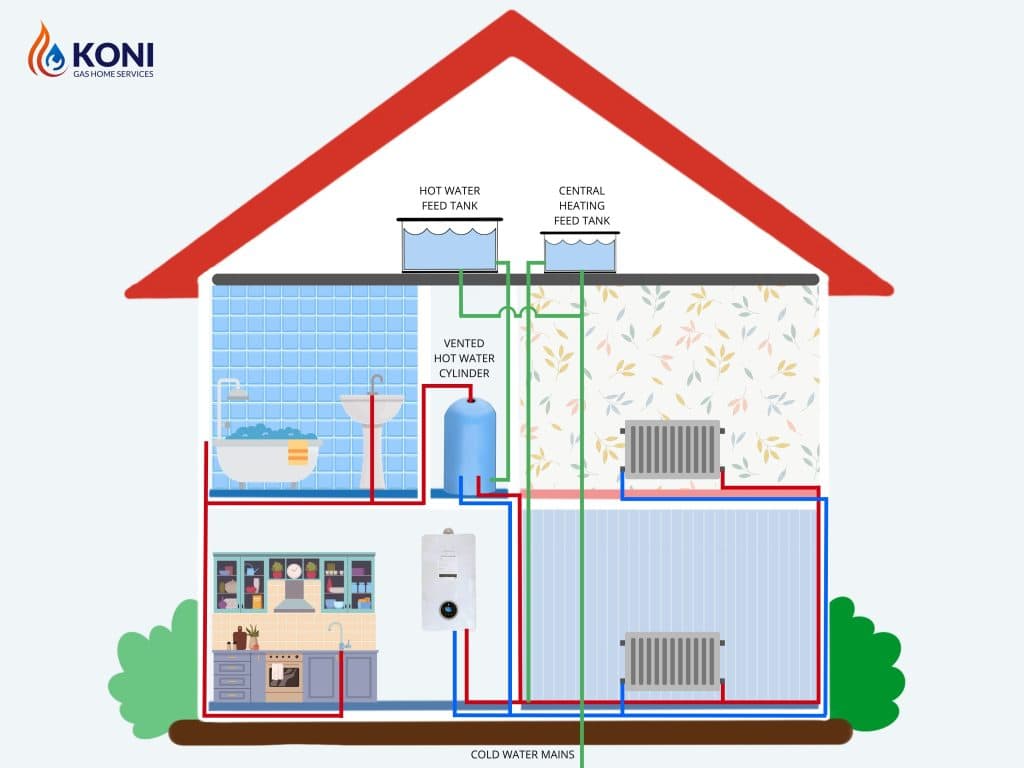
3. Regular Boilers (Vented)
Regular boilers are the traditional choice and are suitable for older homes with existing heating systems. They require a separate hot water cylinder and a cold water storage tank. Regular boilers are known for their reliability and compatibility with older radiator systems. They provide excellent water pressure and are capable of supplying hot water to multiple outlets simultaneously.
For example, a large Victorian house with an existing heating system and ample space for storage tanks would be best suited for a regular boiler. The compatibility with older systems and the ability to supply hot water to multiple outlets make it an ideal choice.
Condensation and non-condensation boilers:
When it comes to boiler installations, there are two other main types to consider: condensation and non-condensation boilers. These boilers are two different types of boilers based on their efficiency and how they handle the waste gases produced during the combustion process. Condensation boilers are known for their higher efficiency and energy savings, while non-condensation boilers are often more affordable and suitable for properties with lower heating demands.
Condensation boilers, also known as high-efficiency boilers, are designed to extract more heat from the flue gases by condensing the water vapor present in them. This condensation process releases additional heat, resulting in higher efficiency and lower fuel consumption. Non-condensation boilers, on the other hand, do not utilize this condensation process and therefore have lower efficiency levels. They release the waste gases directly into the atmosphere without extracting any additional heat. While non-condensation boilers are generally less efficient, they are often more affordable and suitable for properties with lower heating demands. Condensation boilers, although more expensive, offer greater energy savings and are ideal for homes requiring higher heating outputs.
Summary:
Choosing the right type of boiler for your home’s heating needs is crucial for optimal comfort and efficiency. Combi boilers are compact and provide hot water on demand, making them suitable for smaller homes. System boilers are ideal for larger homes with higher hot water demand, while regular boilers are best suited for older homes with existing heating systems. By considering factors such as space availability, hot water demand, and compatibility with existing systems, you can determine the most suitable boiler to install for your home.




